#🌋 LLaVA: Large Language and Vision Assistant
LLaVA (or Large Language and Vision Assistant) is a pioneering open-source multimodal model. Despite its training on a relatively small dataset, LLaVA exhibits exceptional abilities in understanding images and answering questions about them. LLaVA exhibits behaviors similar to multimodal models like GPT-4V from OpenAI.
LLaVA features a straightforward network structure and low fine-tuning costs. It allows any research group, enterprise, or individual to construct their own multimodal model.
LLaVA has three versions: 1.0, 1.5, and 1.6 (LLaVA-NeXT). The most recent and powerful version, LLaVA-v1.6-13B, is currently available for free on Instill Model.
#New in LLaVA-v1.6
According to the original blog, LLaVA-v1.6 has several improvements in comparison to LLaVA-v1.5:
- Increasing the input image resolution to 4x more pixels. This allows it to grasp more visual details. It supports three aspect ratios, up to 672x672, 336x1344, 1344x336 resolution.
- Better visual reasoning and Optical Character Recognition (OCR) capability with an improved visual instruction tuning data mixture.
- Better visual conversation for more scenarios, covering different applications. Better world knowledge and logical reasoning.
- Efficient deployment and inference with SGLang.
Along with performance improvements, LLaVA-v1.6 maintains the minimalist design and data efficiency of LLaVA-v1.5. It re-uses the pretrained connector of LLaVA-v1.5, and still uses less than 1M visual instruction tuning samples. The largest 34B variant finishes training in ~1 day with 32 A100s. Code, data, model will be made publicly available.
#Implementing LLaVA with the Instill Model: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to utilize the LLaVA-v1.6-13B model through both Instill Cloud and Instill Core. We'll guide you through the process of making API calls to trigger model inferences and how to set up the model locally for more advanced uses. Whether you're a developer looking to integrate AI capabilities into your project or just interested in exploring what AI can do, this tutorial is designed to provide you with a straightforward path to success.
#Using Instill Cloud
Instill Cloud offers an easy way to try out models via API calls. Here's how you can get started:
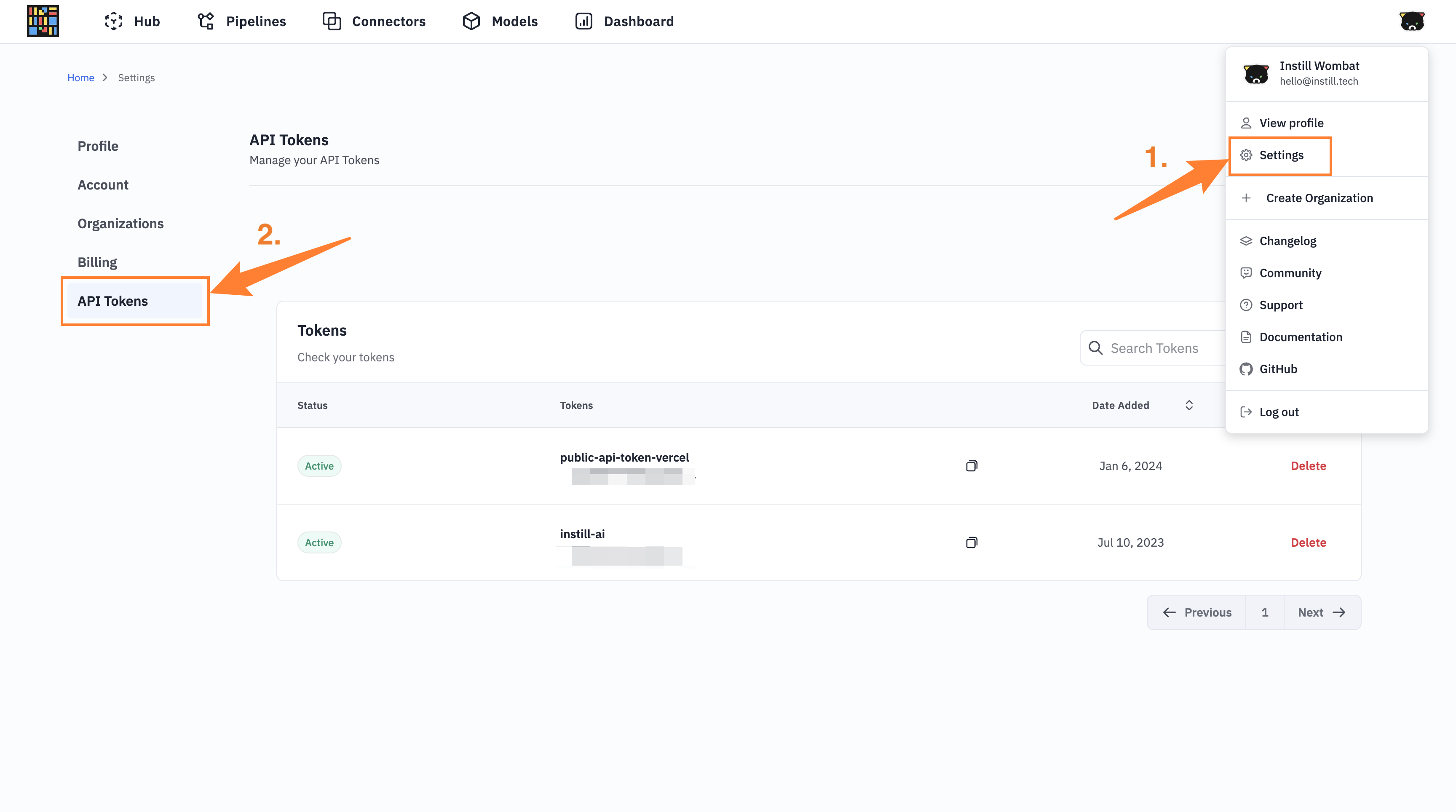
#Step 1: Obtain an API Token
- Sign in to Instill Cloud and navigate to the Settings section.
- Click on API Tokens and generate a new token. Make sure to copy this token for later use.
#Step 2: Choose Your Model
On the API Reference Page, select the "Trigger model inference" option. This tutorial uses Shell as an example, but instructions are available for various programming languages.
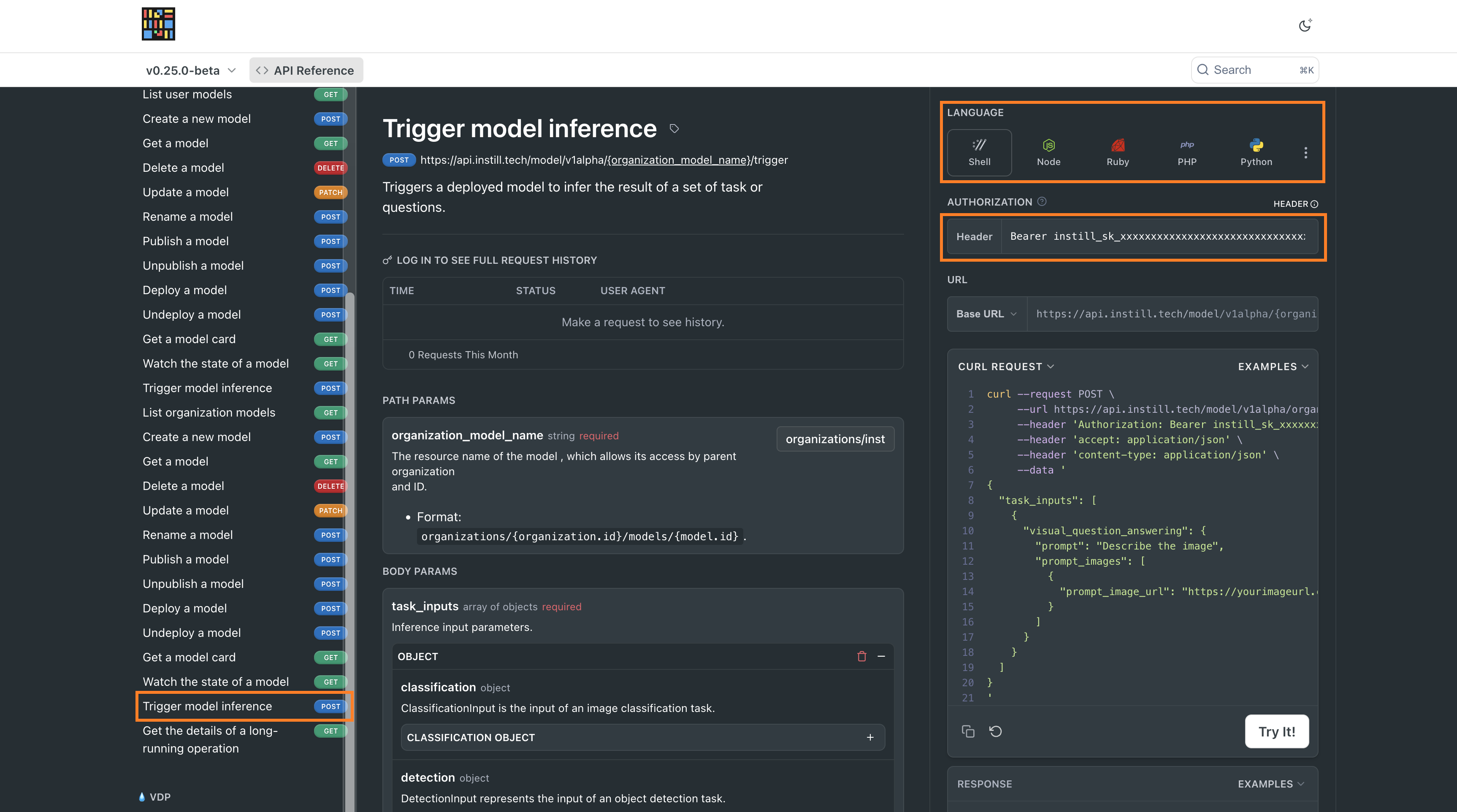
#Step 3: Fill in the Required Fields
You'll need to provide specific information to make the API call:
- Authorization: Enter the token with the
Bearerprefix, e.g.Bearer+'YOUR_API_TOKEN'(attained from Instill Cloud). - PATH PARAMS
- organization_model_name: Use
organizations/instill-ai/models/llava-1-6-13bfor the LLaVA-v1.6-13B model.
- organization_model_name: Use
- BODY PARAMS
- task_inputs: Select
VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING OBJECT.- prompt: Enter your question for the model.
- prompt_images: Provide image data. You can use either:
- prompt_image_url: URL of the image to analyze.
- prompt_image_base64: Base64-encoded image data.
- task_inputs: Select
#Step 4: Execute the API Call
After filling in the fields, click Try It!. You'll receive a curl command similar to the following, which you can run in your terminal:
curl --request POST \ --url https://api.instill.tech/model/v1alpha/organizations%2Finstill-ai%2Fmodels%2Fllava-1-6-13b/trigger \ --header 'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_TOKEN' \ --header 'accept: application/json' \ --header 'content-type: application/json' \ --data '{ "task_inputs": [ { "visual_question_answering": { "prompt": "Describe the image", "prompt_images": [ { "prompt_image_url": "https://yourimageurl.com/image.jpg" } ] } } ]}'
#Using Instill Core
For those looking to run models locally or on their servers, Instill Core provides a robust solution.
#Prerequisites
- Require GPU to run locally
- Install Docker on your machine and open Docker and ensure it's running on your machine.
- Have basic knowledge of using terminal or command prompt.
#Step 1: Setting Up Your Local Environment
Launch Instill Model Locally:
- Clone the Instill Core repository and navigate into the project directory:
$ git clone -b v0.29.0-beta https://github.com/instill-ai/instill-core.git && cd instill-core
- Launch all services with:
make all
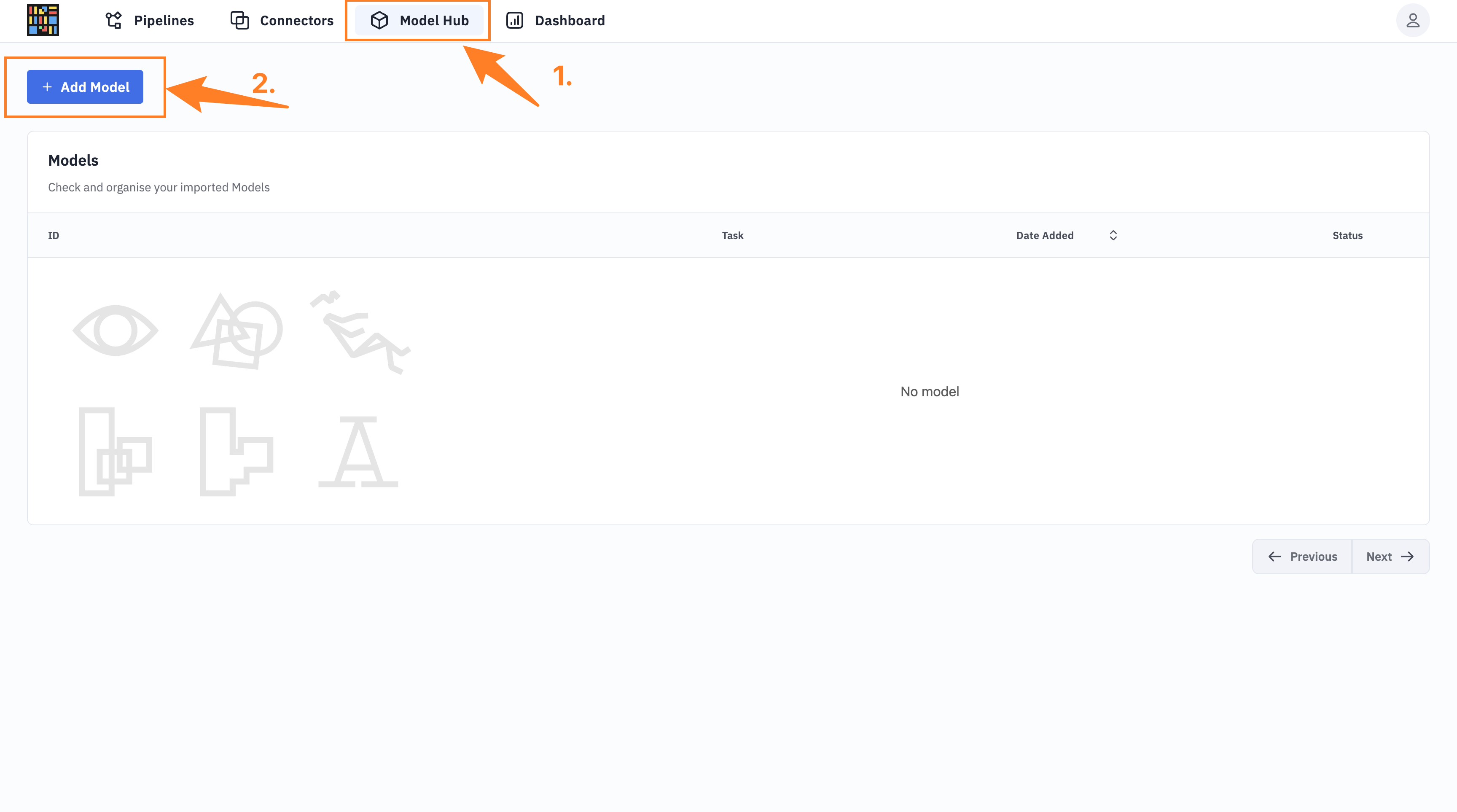
#Step 2: Adding a Model
You can add models either through the console at http://localhost:3000/ or via API.
Via Console
- Log in with username admin and the default password password (you can change this later).
- Navigate to "Model Hub" > "Add Model" and enter the model details as found on the GitHub repository.
Via API
- Obtain an API token from the console by navigating to http://localhost:3000/ > Settings > API Tokens.
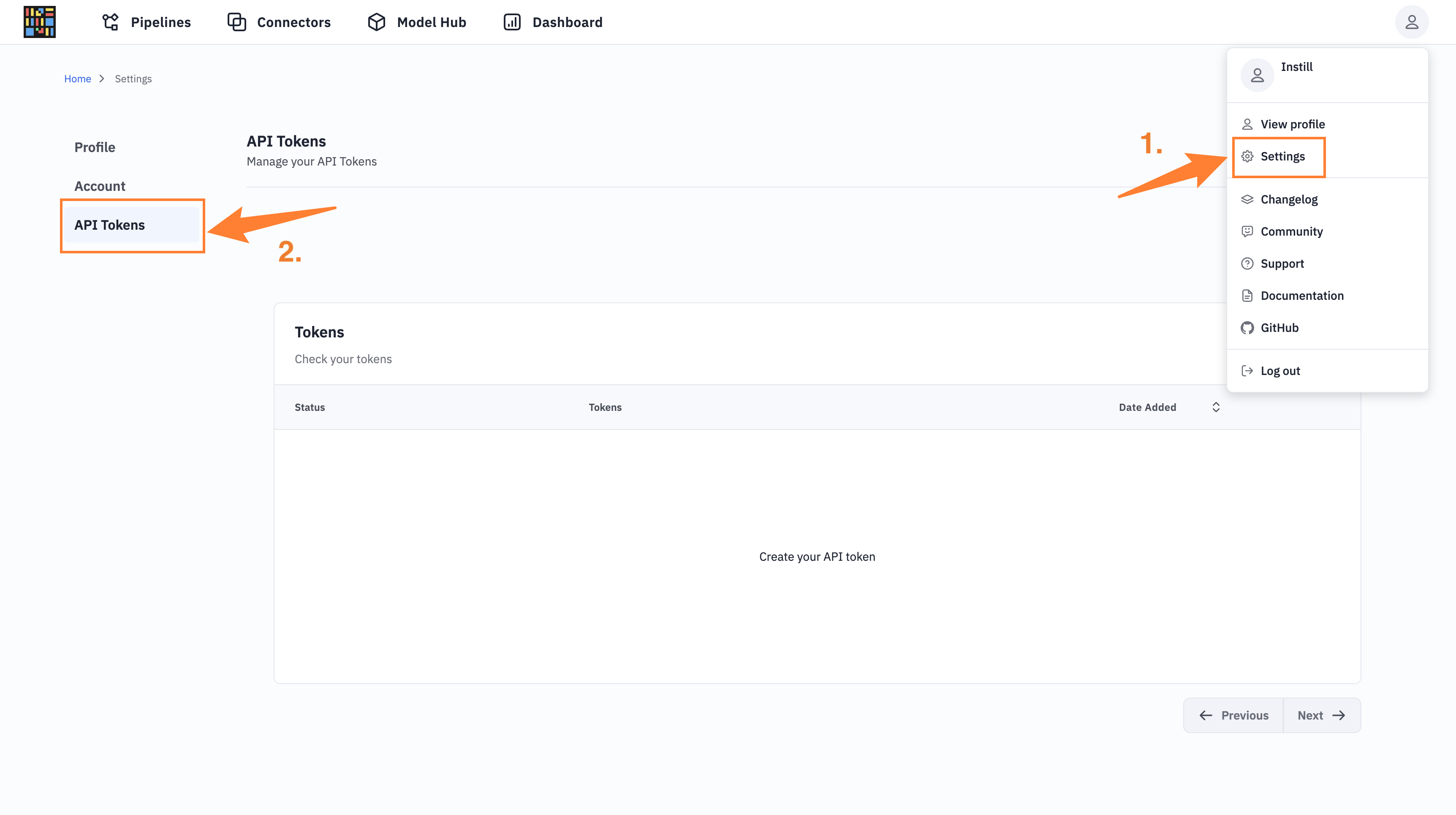
- Go to the API Reference Page to create a new model with the following details:
- Authorization: Enter the token with the
Bearerprefix, e.g.Bearer+'YOUR_API_TOKEN'(attained from http://localhost:3000/). - PATH PARAMS
- user_name: Use
users/admin.
- user_name: Use
- BODY PARAMS
-
id: Enter an ID for your model.
-
task: Select
TASK_VISUAL_QUESTION_ANSWERING. -
model_definition: Use
model-definitions/github. -
configuration: Provide the model's repository and tag details. In this case, it would be
repository:instill-ai/model-llava-13b-dvctag:f16-gpuAuto-transformer-ray-v0.8.16
-
- Authorization: Enter the token with the
#Step 3: Triggering Model Inference
With your model added, you can now trigger model inferences. Here's a curl command example for model inference:
curl --location 'http://localhost:8080/model/v1alpha/users/admin/models/llava-1-6-13b/trigger' \--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \--header 'Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_TOKEN' \--data '{ "task_inputs": [ { "visual_question_answering": { "prompt": "Describe the image", "prompt_images": [ { "prompt_image_url": "https://yourimageurl.com/image.jpg" } ] } } ]}'
By following these steps, you can easily use the LLaVA-v1.6-13B model through Instill Cloud for simple API calls or set it up locally using Instill Core for more extensive testing and development.
#Try it out
Visual Assistant
Ask about an image, get magical answers.
The unusual aspect of this image is that a man is standing on a folding table that is strapped to the back of a yellow taxi, ironing clothes. It is not common to see someone doing laundry in such an unconventional setting, especially while in traffic. The presence of a taxi and the man's position on the table make the scene quite peculiar and eye-catching, as it is not a typical scenario one would expect to see in everyday life.
#Showcases
Let's compare the results generated by LLaVA-v1.5-13B and LLaVA-v1.6-13B!
#Captioning an image
We’re going to ask models to come up with a caption for the following image:
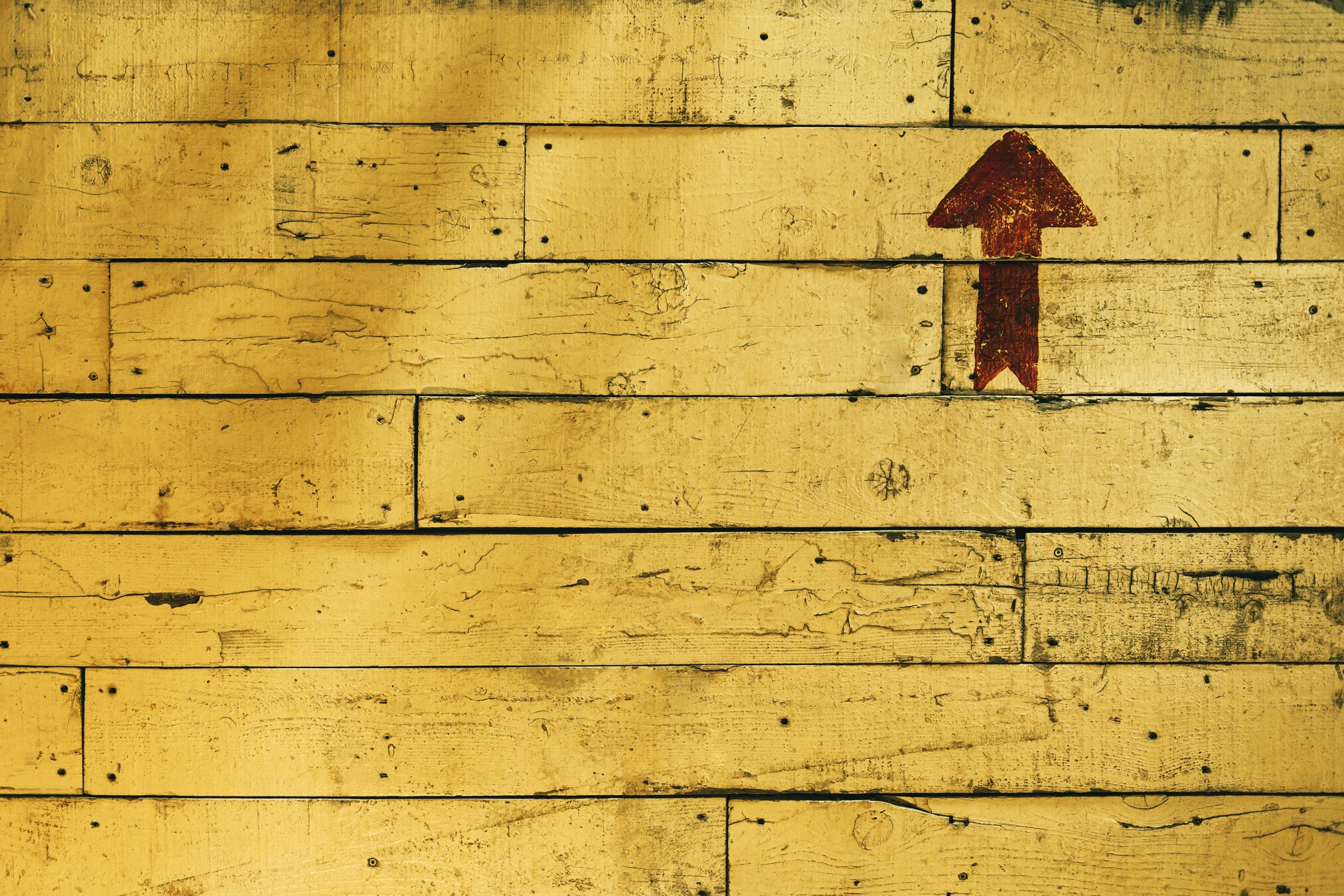

Prompt = Create a caption for this image
LLaVA-v1.5-13B OUTPUT
A yellow plank of wood with a red arrow pointing upwards.
LLaVA-v1.6-13B OUTPUT
Explore new horizons: Your next adventure is just a few steps away.
#Reading the image
Next up, let’s see if the models can read the text from an image.

Prompt = What text is written on this image?
LLaVA-v1.5-13B OUTPUT
The text written on this image is "Difficult Roads Lead to Beautiful Destinations.
LLaVA-v1.6-13B OUTPUT
The text on the image reads, "DIFFICULT ROADS LEAD TO BEAUTIFUL DESTINATIONS."
#Extracting code from an image
Can it extract code from an image? Nowadays, many people post code snippets as images on social media, making it difficult to reuse the code. Perhaps LLaVA can be a solution to this problem.
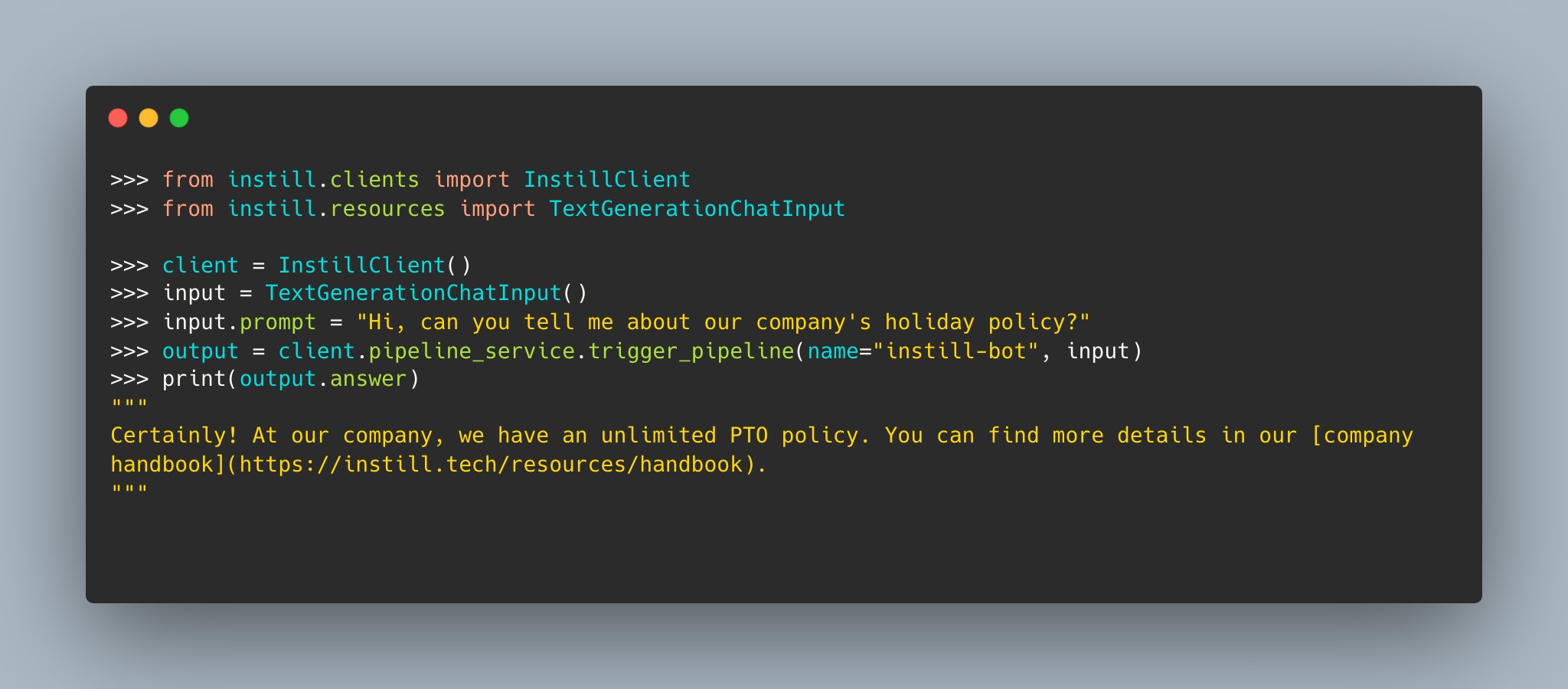
Prompt = Extract the code from this image
LLaVA-v1.5-13B OUTPUT
The image shows a computer screen displaying a code in a programming language. The code consists of multiple lines, with some of them highlighted in yellow. The code appears to be related to a chat application, as it includes phrases such as "instill client" and "text generation chat input." The code also contains information about a company's holiday policy.
LLaVA-v1.6-13B OUTPUT
Here's the text from the image:
Please note that without the context of the environment in which this code is being run, it's difficult to provide an accurate interpretation of what the code is doing. Additionally, the
InstantiateClientmodule or class is not defined in the code snippet, so it appears to be a placeholder or an assumed module for the purposes of the example code.
#Understanding a diagram
Let’s see if it can explain this diagram
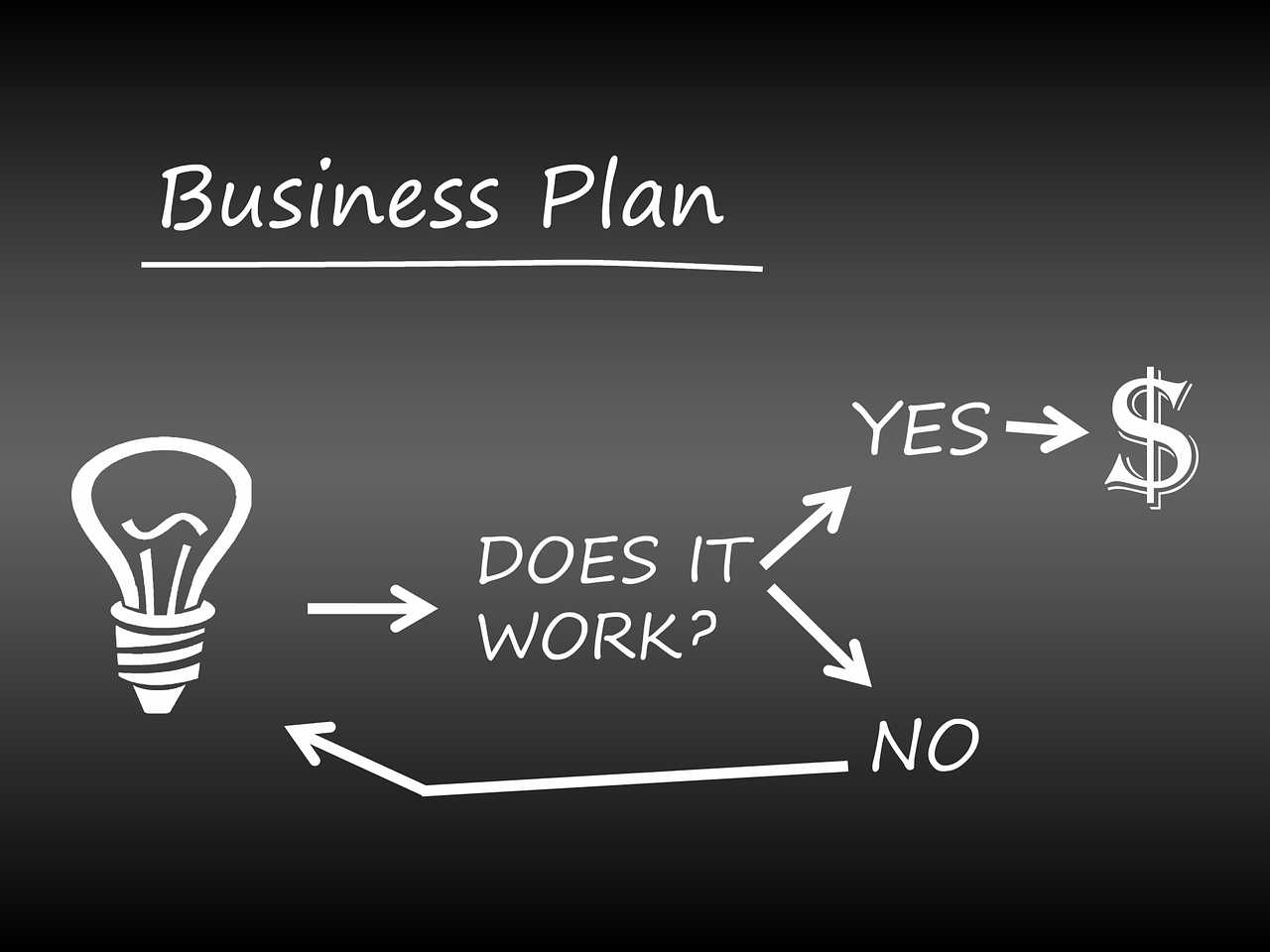
Prompt = Describe the meaning of the diagram
LLaVA-v1.5-13B OUTPUT
The diagram is a flowchart that represents a business plan. It consists of several arrows and questions, which are meant to guide the reader through the process of creating a business plan. The flowchart starts with a question, "Does it work?", followed by a series of arrows pointing to different directions, indicating various aspects of the business plan. The questions and arrows are intended to help the reader think critically about the plan and make informed decisions. The flowchart is designed to be a visual representation of the business planning process, making it easier to understand and follow.
LLaVA-v1.6-13B OUTPUT
The diagram depicts a simple decision-making or problem-solving process using a question format that is often associated with the "light bulb" moment of sudden insight. It shows a three-step sequence with a light bulb icon, which represents an idea, and three branches leading from it.
- The first step asks, "Does it work?", which suggests testing a new idea or approach.
- If the answer to this question is negative, the second branch leads to the question, "Does it work?", indicating that the same process is repeated if the initial idea does not prove effective.
- If the answer to the second question is no, the third branch leads to "No" and the process ends. This suggests that if the idea does not work after two attempts, it may be concluded that the idea is not viable or effective.
- If the answer to the first question is positive, meaning the initial idea is deemed to work, the process moves to the second step, which asks, "Does it work?" again. This implies that the idea is tested again, perhaps to confirm the result or to refine the idea further.
- If the answer to the second question is still positive, the process leads to the third step, "Yes", and the process ends, indicating that the idea is considered to be effective or successful.
The diagram uses a minimalist approach to convey the concept of iterative problem-solving and the importance of testing and confirming the effectiveness of an idea or approach before implementing it.
#Acknowledgements
We'd like to extend our special thanks to Replicate for providing us with LLaVA-v1.5-13B resources to conduct this experiment. For those interested in testing LLaVA-v1.5-13B, you can access it on Replicate's website here.
#Conclusion
LLaVA's remarkable image understanding and visual problem-solving capabilities indicate its potential for wide-ranging applications. However, Vision Language Model (VLM) model outputs can be uncertain and their accuracy fluctuates based on the complexity and specificity of the task. This highlights the need for stable use, particularly in critical applications where precision is vital.
LLaVA can significantly contribute to fields like media content creation by generating descriptions and explanations, potentially enhancing accessibility and user engagement. Its OCR capabilities can also be employed in document processing and data extraction tasks, potentially revolutionizing administrative workflows. Plus, its code extraction function could be a valuable educational tool, aiding learners in understanding code snippets shared as images.
Despite these extensive application prospects, users should comprehend LLaVA's limitations and non-deterministic features, ensuring thorough validation and testing in their specific scenarios. Multimodal models like LLaVA represent a crucial step in AI development, emphasizing the ongoing need for users and VLM developers to enhance accuracy and reliability while promoting innovative solutions.
For those interested in deploying or experimenting with LLaVA, Instill AI offers services that facilitate easy integration and testing of this powerful model.

